The ______ receives lymph from the right side of the head, neck, and thorax, and from the right upper limb.
right lymphatic duct
Name the lymphatic system organ that shrinks and becomes non-functional with age.
The filtering of lymph and the initiation of immune responses to foreign material are functions of what organ(s)?
Lymphatic nodules are encapsulated lymphatic organs.
lymphatic nodules are clusters of immune cells that lack a connective tissue capsule.
Which are the lymphatic organs of the oral cavity and pharynx?
Match each statement with the appropriate lymphatic structure.
(find the functions of lymph node, thymus, spleen)
Lymph node: Filters lymph; initiates immune responses
Thymus: Site of maturation of T lymphocytes
Spleen: Filters blood; initiates immune responses
Cytotoxic T cells mount an immune response against __________.
cells that display foreign proteins on their surface
Cytotoxic T cells produce __________ which creates holes in the cell membranes of target cells.
How do cytotoxic T cells recognize that a cell is infected with a virus and needs to be destroyed?
The presence of foreign (viral) proteins on the target cell surface.
The receptors on cytotoxic T cells bind to __________.
viral antigens and class I MHC.
Foreign substances that elicit an immune response are called __________.
Macrophages secrete __________ which then activates __________ .
interleukin-1 ; helper T cells
Cytotoxic T cells target and destroy __________.
infected "self" cells
Helper T cells stimulate the proliferation of __________.
cytotoxic T cells and B cells
The secondary immune response to a previously encountered pathogen is swifter and stronger than the primary immune response.
Complete the sentences describing the functions of the lymphatic system.
The lymphatic system is involved in the absorption of __________ from the digestive system.
Label the features of the capillary and lymphatic bed.
This flow chart diagrams the series of structures involved in lymphatic drainage. Indicate the correct order of vessels.
Lymphatic capillary -> afferent lymphatic vessel -> lymph node -> efferent lymphatic vessel -> lymphatic trunk -> collecting duct -> subclavian vein
Complete the sentences describing tissue fluid and the formation of lymph.
Lymph drainage is important for what functions?
absorption of dietary fats,
return of small proteins from tissue fluid to blood,
transport of foreign particles from tissue fluid to lymph nodes
The absence or blockage of lymph vessels in a body region leads directly to what condition?
This image shows a lymphatic vessel. The arrows indicate valves found in these vessels. Based on your understanding of the function of lymphatic valves, in which direction would lymph be flowing through the vessel shown?
From bottom of image toward top of image
Exercise is associated with an increase in lymph movement.
This figure shows the areas of lymphatic drainage. Correctly indicate the collecting duct that drains each area.
Lymph eventually is returned to the circulation at what blood vessels?
Right and left subclavian veins.
What is the role of skeletal muscle contractions in the flow of lymph?
skeletal muscles contraction compress lymphatic vessels, encourages the lymph to flow toward the upper thorax
Label the components of the sectioned lymph node.
Indicate where in the lymph nodes the listed cell types are found by dragging labels to the appropriate boxes. Some labels are used more than once.
List the function(s) of lymph nodes.
In the cadaver image shown, name the group of lymph nodes highlighted in yellow.
Axillary lymph nodes
Label the clusters of lymph nodes.
For each description, indicate the correct group of lymph nodes.
In the cadaver image, identify the lymphatic structure highlighted in yellow.
In this image of the abdominal cavity of a cadaver, name the structure highlighted in yellow.
Label the thymus, spleen, and neighboring structures and organs.
Label the tissues and vessels of the spleen.
Label the regions within the spleen.
Classify each item as a feature of innate defense or adaptive defense.
The ______ defense mechanisms target specific pathogens.
In contrast, the more general defenses that protect against many types of pathogens are the _____ defense mechanisms.
Consider the types of defense. Drop each label into the flow chart to indicate whether it is a first, second, or third line of defense.
A chemical called endogenous pyrogen may be released from lymphocytes that are responding to a pathogen. What does this compound cause?
Natural killer (NK) cells are what type of cell?
Name the cells included in the mononuclear phagocytic system
Match the description with the correct chemical barrier.
Name the innate defense that involves vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, resulting in the influx of blood, blood cells, and fluid to an area of injury or infection.
The figure illustrates the sites of lymphocyte precursor production, the site where T cells are processed, the site where B cells are processed, and an eventual location for the lymphocytes. Label each site.
Place the labels describing the locations of origin, development, and action of lymphocytes in the correct location on the figure.
Indicate the characteristics of the label is associated with B cells or T cells
Complete the sentences describing the types of T cells
Drag each label to the appropriate box to indicate if the label is associated with B cells or T cells
Indicate the cells that can function as antigen-presenting cells.
Dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells
This figure illustrates the activation of B and T cells. Label the cells that are involved in the process.
This figure illustrates the process of stimulation and proliferation of B cells.
What term refers to any molecule that elicits an immune response?
Cells such as macrophages can process foreign antigens and attach them to their cell surface in order to assist in activation of T cells. What are cells that have this function called?
Place the events leading to T cell activation in the correct order.
Match the description with the correct type of cytokine.
Cell membrane proteins called ______ major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens are found on antigen-presenting cells, thymus cells, and activated T cells.
The _______ MHC antigens are found on membranes of all body cells, except red blood cells.
Class I MHC antigens are found in the membranes of_____ .
Class II MHC antigens are found in the membranes of ___________.
all body cells except RBCs
antigen-presenting cells, thymus cells, and activated T cells
The body is equipped with several mechanisms that function to prevent infection by pathogens. These mechanisms are referred to as the innate (nonspecific) defenses. They include mechanical and chemical barriers, phagocytic and natural killer cells, and the processes of inflammation and fever.
1. Interferons and complement proteins are examples of __________.
2. The changes that occur in infected or injured tissue (redness, swelling, heat, pain) are due to the process of __________.
3. Mechanical barriers include __________.
1. Chemical barriers
2. Inflammation
3. Skin and mucous membranes
The adaptive defenses are those responses by immune cells that target specific foreign antigens, with the purpose of destroying or inactivating the antigen. Review the roles of the various types of immune cells and answer the questions below. In the next activity, you will view an animation showing the steps in an immune response.
1. The primary cells of the immune response are the T and B cells. T and B cells are what type of cell?
2. Macrophages have a role in both innate and adaptive defenses. What is the function of macrophages during infection by a pathogen?
3. Phagocytic cells such as macrophages digest a pathogen, then insert a bit of pathogenic antigen on their cell membrane. In this role, these cells are described as being __________ cells.
1. Lymphocytes
2. To phagocytize the pathogen
3. Antigen-presenting
1. A macrophage that has phagocytized and displayed the antigen on its surface is acting as a(n) __________.
2. Macrophages that are displaying a pathogenic antigen will interact with __________ which then continue the immune response.
3. Name the immune cell that interacts with and kills an infected "self" cell.
4. B cells are activated by (1) the binding of their antigen and (2) interaction with __________.
5. What type of cell produces antibodies?
6. Memory cells are involved in the __________ immune response.
1. Antigen-presenting cell
2. Helper T cells
3. Cytotoxic cells
4. Helper T cells
5. Plasma cells
6. Secondary
Indicate whether the listed components of an immune response interact directly with an antigen, or if presentation of the antigen by an antigen-presenting cell is required. Labels may be used twice.
Complete the sentences describing the various classes of immunoglobulins, or antibodies.
Complete the sentences describing antibodies.
Fill in the blanks in the figure legend, indicating the identity of the different colored segments of the antibody molecule.
Each label is used twice.
Drop each label into the appropriate box, indicating which class of immunoglobulin is being described. Some labels are used more than once.
What class of immunoglobulin is involved in immediate-reaction allergic reactions?
Memory T and B cells function in what type of response?
Secondary immune responseCorrect
The labels describe either a primary or secondary immune response. Drop each label into the appropriate bo
Immunity acquired with the injection of antibodies from another source is called ____
Immunity resulting when one's own immune system responds to an antigen encountered through normal routes is called______
Immunity in a newborn due to the passing of maternal antibodies through the placenta is called______
Immunity that occurs following vaccination with an antigen is called ______
artificially acquired passive immunity
naturally acquired active
naturally acquired passive
artificially acquired active
Complete the sentences describing the different types of immunity.

With aging, there is no decrease in the number B cells, and only a slight decrease in the number of T cells.
What is the first component(s) of the immune system to decline with age?
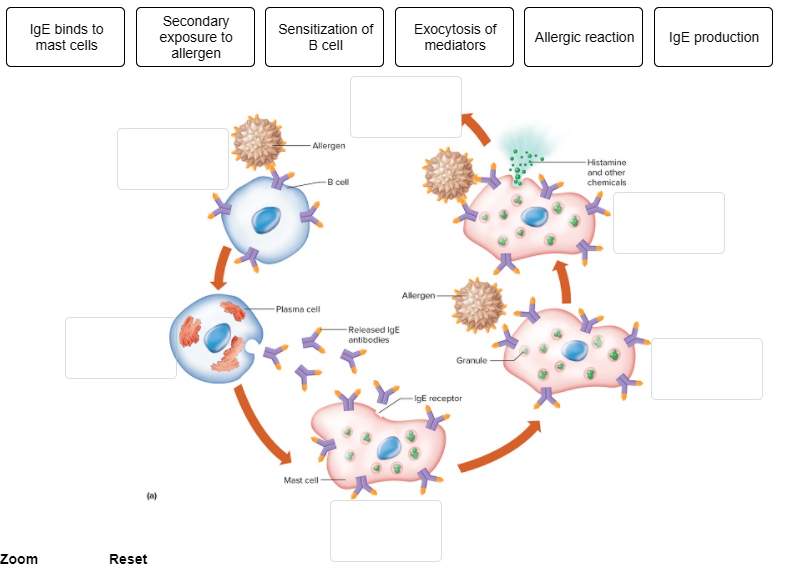
Put the steps that occur during an immediate-reaction allergic response in the correct order.
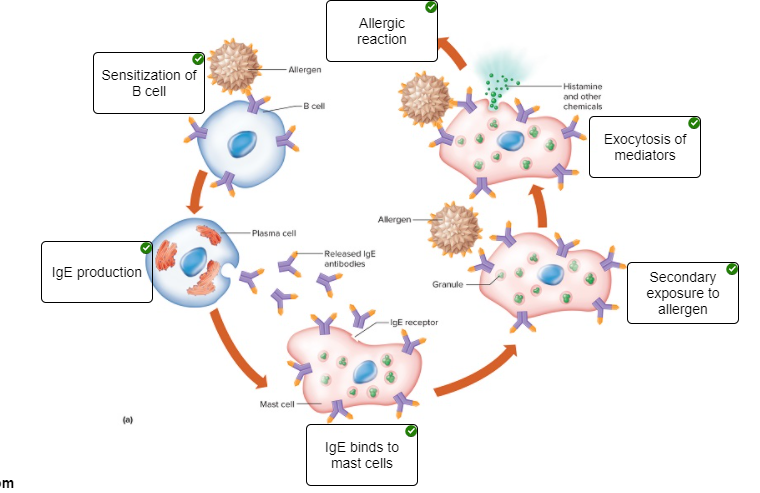
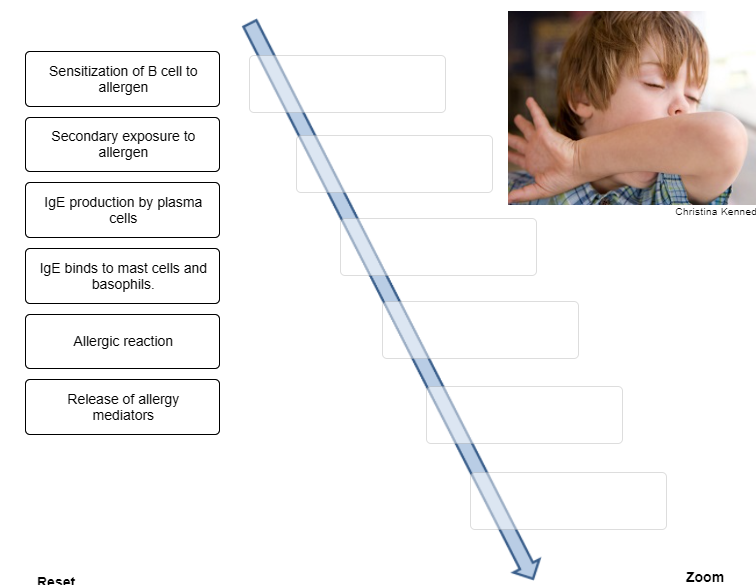
Place the steps that occur during an immediate-reaction allergic response in the correct order.
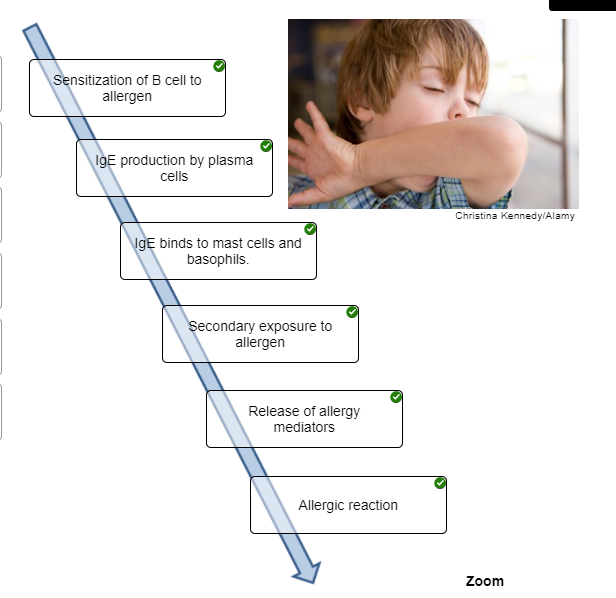
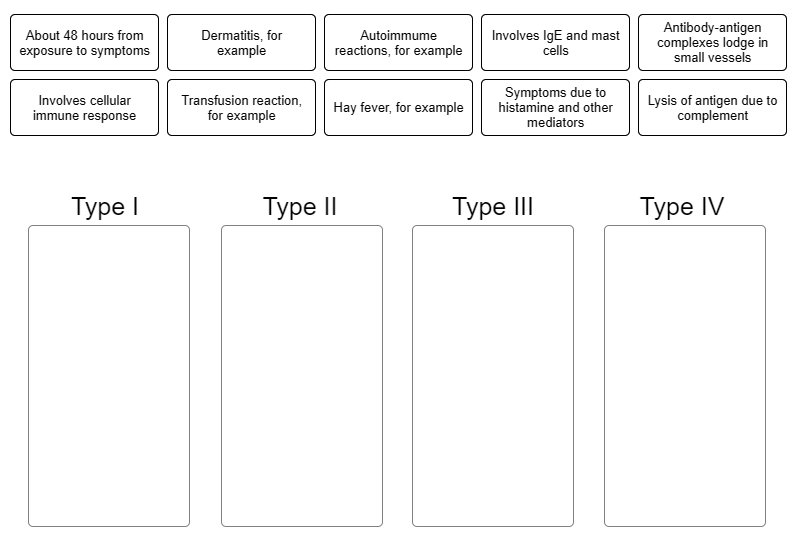
Indicate characteristic into the appropriate box, describing each type of hypersensitivity.